| 1. Voice assistant for basic linux commands |
| 2. Create sine wave animation |
| 3. Show trajectory animation using the position (X,Y) and time (T) coordinates given in a file |
| 4. Program to convert audio speech into text |
| 5. Create equal spaced members inside a given array |
| 6. How to change 0 to 1 and 1 to 0 inside a matrix |
| 7. Read and print content of excel file |
| 8. Merge two excel files based on a column value (e.g. Barcode Number). Report changes in Status and ChangeLog column in the merged file. |
| 9. Remove lines containing given word from the last paragraph of a file |
| 10. Print value of key press on keyboard |
| 11. Read csv file into dataframe and print its elements |
| 1. Voice assistant for basic linux commands |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import speech_recognition as sr
from gtts import gTTS
import pygame
import os
def listen():
r = sr.Recognizer()
with sr.Microphone() as source:
r.adjust_for_ambient_noise(source)
audio_text = r.listen(source)
data=""
try:
data = r.recognize_google(audio_text,language = "en-US")
print("You said: " + data)
except sr.UnknownValueError:
print("Google Speech Recognition did not understand audio")
except sr.RequestError as e:
print("Request Failed; {0}".format(e))
return data.casefold()
def respond(audio_string):
print(audio_string)
convert = gTTS(text= audio_string, lang="en", slow=False)
convert.save("speech.mp3")
pygame.mixer.init()
pygame.mixer.music.load("speech.mp3")
pygame.mixer.music.play()
def voice_assistant(data):
answer = True
response_text = ""
data_set = set(data.split())
if ({"working"}).issubset(data_set):
if "folder" in data_set or "directory" in data_set:
cwd = os.getcwd()
response_text = "current working directory is " + cwd
print(response_text)
respond(response_text)
else:
response_text = "question format - current working directory or current working folder"
respond(response_text)
elif "make" in data_set or "create" in data_set:
if "folder" in data_set or "directory" in data_set:
directory_name = get_keyword_of_string(data,2)
try:
path = os.path.join(".",directory_name).lower()
print(path)
os.mkdir(directory_name)
response_text = directory_name + " created successfully"
except FileExistsError:
response_text = directory_name + " already exists"
except PermissionError:
response_text = "Unable to create " + directory_name + " Permission denied"
print(response_text)
respond(response_text)
else:
response_text = "question format - create folder or create directory or make folder or make directory"
respond(response_text)
elif ({"many","files","in"}).issubset(data_set):
idx = -1 #index for folder or directory
mylist = data.split()
length = len(mylist)
folder_name = ""
path = ""
flag = False
response_text = "question format - how many files in current folder OR how many files in folder foldername"
print(length)
if "folder" in data_set:
idx = get_index_of_item_in_list(mylist, "folder")
if "directory" in data_set:
idx = get_index_of_item_in_list(mylist, "directory")
if idx == -1:
respond(response_text)
else:
if idx == length-1 and "current" in mylist:
folder_name = "."
path = "."
elif idx == length-2:
folder_name = mylist[length-1]
path = os.path.join(".",folder_name)
else:
respond(response_text)
flag = os.path.isdir(path)
if flag == False:
path = os.path.join(".",folder_name.lower())
flag = os.path.isdir(path)
if flag == True:
folder_name = folder_name.lower()
else:
path = os.path.join(".",folder_name.capitalize())
flag = os.path.isdir(path)
if flag == True:
folder_name = folder_name.capitalize()
print(path)
if flag == True:
filelist = list_files_of_directory(path)
print(filelist)
num = len(filelist)
response_text = "There are " +str(num)+ " files in folder " + folder_name
print(response_text)
respond(response_text)
else:
response_text = "folder "+folder_name+" does not exist"
respond(response_text)
elif ({"is","in","folder"}).issubset(data_set):
path = ""
flag = False
folder_name = ""
file_name = ""
mylist = data.split()
response_text = "question format - Is filename in current folder OR Is filename in folder foldername"
idx_is = get_index_of_item_in_list(mylist,"is")
idx_in = get_index_of_item_in_list(mylist,"in")
idx_folder = get_index_of_item_in_list(mylist,"folder")
length = len(mylist)
print(length)
for word in mylist[idx_is+1:idx_in]:
if word == "dot":
newword = "."
else:
newword = word
file_name = file_name+newword
print("File="+file_name)
if idx_folder == length-1 and "current" in mylist:
folder_name = "."
path = "."
elif idx_folder == length-2:
folder_name = mylist[length-1]
path = os.path.join(".",folder_name)
else:
respond(response_text)
print("Folder="+folder_name)
flag = os.path.isdir(path)
if flag == False:
path = os.path.join(".",folder_name.lower())
flag = os.path.isdir(path)
if flag == False:
path = os.path.join(".",folder_name.capitalize())
flag = os.path.isdir(path)
if flag == True:
path = os.path.join(folder_name, file_name)
print(path)
check_file = os.path.isfile(path)
if(check_file):
response_text = "yes"
else:
path = os.path.join(folder_name, file_name.capitalize())
check_file = os.path.isfile(path)
if(check_file):
response_text = "yes"
else:
response_text = "no"
print(response_text)
respond(response_text)
else:
response_text = "folder "+folder_name+" does not exist"
respond(response_text)
elif ({"exit"}).issubset(data_set) or ({"stop"}).issubset(data_set):
answer = False
response_text = "bye for now"
print("bye for now")
respond(response_text)
else:
if(len(data_set)):
response_text = "I can asssist in folder related commands only"
print(response_text)
respond(response_text)
return answer
def get_keyword_of_string(string_text, index):
mylist = string_text.split()
return(mylist[index])
def get_index_of_item_in_list(thelist, item):
i = 0
found = False
for x in thelist:
if x == item:
found = True
break
i = i + 1
if found == False:
return -1
else:
return i
def list_files_of_directory(path):
print(path)
filelist = []
with os.scandir(path) as it:
for entry in it:
if not entry.name.startswith("."):
if entry.is_file():
filelist.append(entry.name)
return filelist
respond("As voice assistant, what can I do for you? say exit to stop")
listening = True
while listening == True:
data = listen()
listening = voice_assistant(data)
|
Instructions
------------
Following python packages are needed (can be installed using)
1. pip3 install speechRecognition
2. pip3 install gtts
3. pip3 install pygame
Run program
-----------
1. save program as - voice_assistant.py
1. chmod +x ./voice_assistant.py [to make it an executable]
2. ./voice_assistant.py
How it works
------------
1. It waits for a question until you ask it to "stop". So voice assistant work in "infinite loop" till you ask it to stop
2. It will voice "I failed to understand. Please ask again" if audio is not clear or the question is not interpreted correctly by the voice assistant.
a) Words with similar sound i.e homophone can causes the voice assistant not understanding it clearly (depends on accent / mic quality or location etc)
b) It will print a message of the "audio" question it heard on the terminal window. So you can check for discrepancy between spoken questions and voice assistant interpretation.
Questions asked and audio response of voice assistant (correctly answered)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Current working directory OR current working folder
2. Make folder OR make directory OR create folder OR create directory
If the folder already exists, it will respond accordingly i.e. folder already exists
3.
a) How many files in folder
Will give you the count of files in _current_ folder
b) How many files in folder xyz
Will give you the count of files in folder xyz (or any other name). xyz is the sub folder of the current working directory
4.
a) Is file abc.txt in folder
Will answer "yes" id abc.txt exists in _current_ folder else "no"
b) Is file xyz.txt in folder Alpha
Will answer "yes" if xyz.txt exists in sub folder Alpha else "no". Alpha is the sub directory of current working directory
5. Stop
This will stop and exit the voice assistant.
|
| 2. Create sine wave animation |
 |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation #Creating frame with data
from matplotlib.animation import PillowWriter #creating and saving animation
#take 100 equal distance values for x between 0 & 2pi
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
#get corresponding y values as sin(x)
y = np.sin(x)
#Create a figure containing single plot & single axis. single plot i.e. 1 row and 1 column in figure. return the figure and the axes of the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
#Set the x-axis and y-axis view limits. Since sin varies from -1 to 1 .. it is set to -1.1 to 1.1 for y for viewing
ax.set_xlim([0, 2*np.pi]) #set x axis view limits from 0 to 2pi
ax.set_ylim([-1.1, 1.1]) #set y axis view limits from -1.1 to 1.1
#Setting the title, x label, y label for the plot
ax.set_title("Sine Wave Animation")
ax.set_xlabel("x(radians)")
ax.set_ylabel("sin(x)")
#Initialise the plot for data
sinegraph, = ax.plot([],[])
def update_sine(i): #i stand for next value in the frame
sinegraph.set_data(x[:i],y[:i])
return sinegraph,
#Calling update_sine for the display of the graph. The graph gets updated for
#each frame created for each point (x,y) and displayed from start till the
#point corresponding to the frame
#You can change blit to True for faster rendering
#FuncAnimation arguments
# fig : Figure used for drawing
# update_sine : Function to be called for each frame
# frames is int i.e. count of values along x axis. Equivalent to range(len(x))
# So function is called for each value of x from 0 to len(x)-1
# interval=50 : Delay in frame is 50 milli seconds
# repeat=True : Animation repeats when the sequence of frames is completed
# blit : blitting is a technique used to optimize the animation process by only redrawing the parts of the plot that have changed between frames. It significantly speeds up the animation
ani = FuncAnimation(fig,
update_sine,
frames=len(x),
interval=10,
repeat=True,
blit=False)
#When blit=True, the axis lables and marking are not visisble in animation.
#Most likely due to the reason that only changed parts are redrawn in the plot.
print("Creating GIF file for Sine Wave ....")
ani.save("sine_wave_animation.gif", dpi=100, writer=PillowWriter(fps=20))
print("Created GIF for Sine Wave successfully")
plt.show()
|
| 3. Show trajectory animation using the position (X,Y) and time (T) coordinates given in a file |
 |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
from matplotlib.animation import PillowWriter
# Below read_file() function for reading the text file. sep "" is being used as the columns
# are separated by blank space. This function returns the three columns of the files as list
def read_file(filename):
df = pd.read_csv(filename, sep=" ")
a = df["x"].tolist()
b = df["y"].tolist()
t = df["time"].tolist()
return a, b, t
#Assigning the output of read_file (3 columns as list) to three variables
xcoord,ycoord,tcoord = read_file("inward_spiral.txt")
#Initialise the Figure and axes object. Figure represent entire figure and axes
#represent the subplot to draw into
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
#Set the x-axis and y-axis view limits. These limits are set based on the minimum
#and the maximum values in the list + delta (for display to be with in axes bounds)
#define delta a number for seting x & y limits for graphical display.
#0.1 is choosen looking at the values of x & y in the text file
delta = 0.1
x_maxLim = max(xcoord) + delta
x_minLim = min(xcoord) - delta
y_maxLim = max(ycoord) + delta
y_minLim = min(ycoord) - delta
ax.set_xlim([x_minLim, x_maxLim])
ax.set_ylim([y_minLim, y_maxLim])
#Setting the title
ax.set_title("Trajectory Animation")
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
spiralgraph, = ax.plot([],[])
def update_trajectory(i):
spiralgraph.set_data(xcoord[:i],ycoord[:i])
return spiralgraph,
#interval is defined the as the delay between frames. This is calculated based on the
#time coord. Take two consecutive points (here we are taking first 2 points). As time
#is in seconds and we need to pass in milliseconds, the interval is multiplied by 1000
inter_val = int((tcoord[1] - tcoord[0])*1000) # inter_val=10 millisecond
#Calling update_trajectory for the display of the graph. The graph gets updated for
#each frame created for each point (xcoord,ycord) and displayed from start till the
#point corresponding to the frame
#You can change blit to True for faster rendering
ani = FuncAnimation(fig, update_trajectory, frames=len(xcoord), interval=inter_val, repeat=True, blit=False)
#PillowWriter is used to save animation object as GIF file
#fps stand for frame per second.
#10 millisecond = 1 frame (see inter_val above)
#1 second => (1 / 10) * 1000 = 100 frames i.e ideall fps = 100
print("Creating GIF file for Trajectory ....")
#Saving the animation as gif file
ani.save("trajectory_animation.gif", dpi=100, writer=PillowWriter(fps=100))
print("Created GIF for Trajectory successfully")
plt.show()
|
| 4. Program to convert audio speech into text |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import speech_recognition as sr
from gtts import gTTS
r = sr.Recognizer()
text=''
with sr.Microphone() as source:
print("Say something")
r.adjust_for_ambient_noise(source)
audio_text = r.listen(source)
try:
text = r.recognize_google(audio_text,language = 'en-US')
#text = r.recognize_google(audio_text,language = 'hi-IN')
except sr.UnknownValueError:
print('Google Speech Recognition could not understand audio')
except sr.RequestError as e:
print("Could not request results from Google Speech Recognition service; {0}".format(e))
print(text)
#x = text.split()
#num = len(x)
#input_text = "Your sentence has " +str(num)+" words in it"
#print(input_text)
#convert = gTTS(text= text, lang='en', slow=False)
convert = gTTS(text= text, lang='en', slow=False, tld='co.in')
convert.save('output_microphone.mp3')
|
1) You need to have following python modules installed
a) speech_recognition
b) gtts
They can be installed using pip
a)pip install speech_recognition
b)pip install gtts
2) Save the code to a file .. say microphone.py
3) chmod +x microphone.py {Note : it is for making program as an executable}
4) run ./microphone.py
How it works
------------
1) Speak sentences in the microphone once the program prompts for "Say Something"
2) Program will print the spoken sentence on the screen
3) Program will also print "Your sentence has -- words in it."
4) It will create an "output_microphone.mp3" file in the folder.
5) Once you play the file, you will hear the audio of
"Your sentence has -- words in it."
The program makes use of the "recognize_google()" api. So .. when you are running the program, your system must be connected to the internet.
|
| 5. Create equal spaced members inside a given array |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import numpy as np
def create_points_within_array(arr,npoints):
i = 0
nx = np.array([])
for k in arr[i:]:
if(i < len(arr)-1):
a = arr[i]
b = arr[i+1]
c = np.linspace(a,b, num=npoints,endpoint=False)
c = np.delete(c, 0)
if i == 0:
nx = np.append(nx,a)
nx= np.append(nx,c)
nx = np.append(nx,b)
i = i + 1
return nx
x = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
nx = create_points_within_array(x,10)
print("x =",x)
print("nx =",nx)
|
x = [1 2 3 4 5]
nx = [1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2. 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 3. 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 4. 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 5. ]
|
| 6. How to change 0 to 1 and 1 to 0 inside a matrix |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import numpy as np
matrix = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
print("Original Matrix")
print(matrix)
matrix = matrix ^ 1
print("Flipped Matrix")
print(matrix)
|
Original Matrix
[[0 0 0 1]
[0 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 1]]
Flipped Matrix
[[1 1 1 0]
[1 0 0 0]
[1 1 1 0]]
|
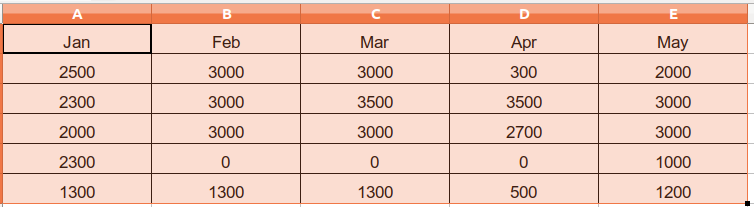
| 7. Read and print content of excel file |
 |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import openpyxl
path="test.xlsx"
wb_obj = openpyxl.load_workbook(path)
sheet_obj = wb_obj.active
row = sheet_obj.max_row
column = sheet_obj.max_column
print("Num Rows:", row,", Num Columns:", column)
print("\nValues of first column")
for i in range(1, row + 1):
cell_obj = sheet_obj.cell(row=i, column=1)
print(cell_obj.value)
print("\nValues of first row")
for i in range(1, column + 1):
cell_obj = sheet_obj.cell(row=2, column=i)
print(cell_obj.value, end=" ")
print("\n\nValue of all cells")
cell_obj = sheet_obj['A1': 'E6']
for cell1, cell2, cell3, cell4, cell5 in cell_obj:
print(cell1.value,"\t",cell2.value,"\t",cell3.value,"\t",cell4.value,"\t",cell5.value)
Output
------
Num Rows: 6 , Num Columns: 5
Values of first column
Jan
2500
2300
2000
2300
1300
Values of first row
2500 3000 3000 300 2000
Value of all cells
Jan Feb Mar Apr May
2500 3000 3000 300 2000
2300 3000 3500 3500 3000
2000 3000 3000 2700 3000
2300 0 0 0 1000
1300 1300 1300 500 1200
|
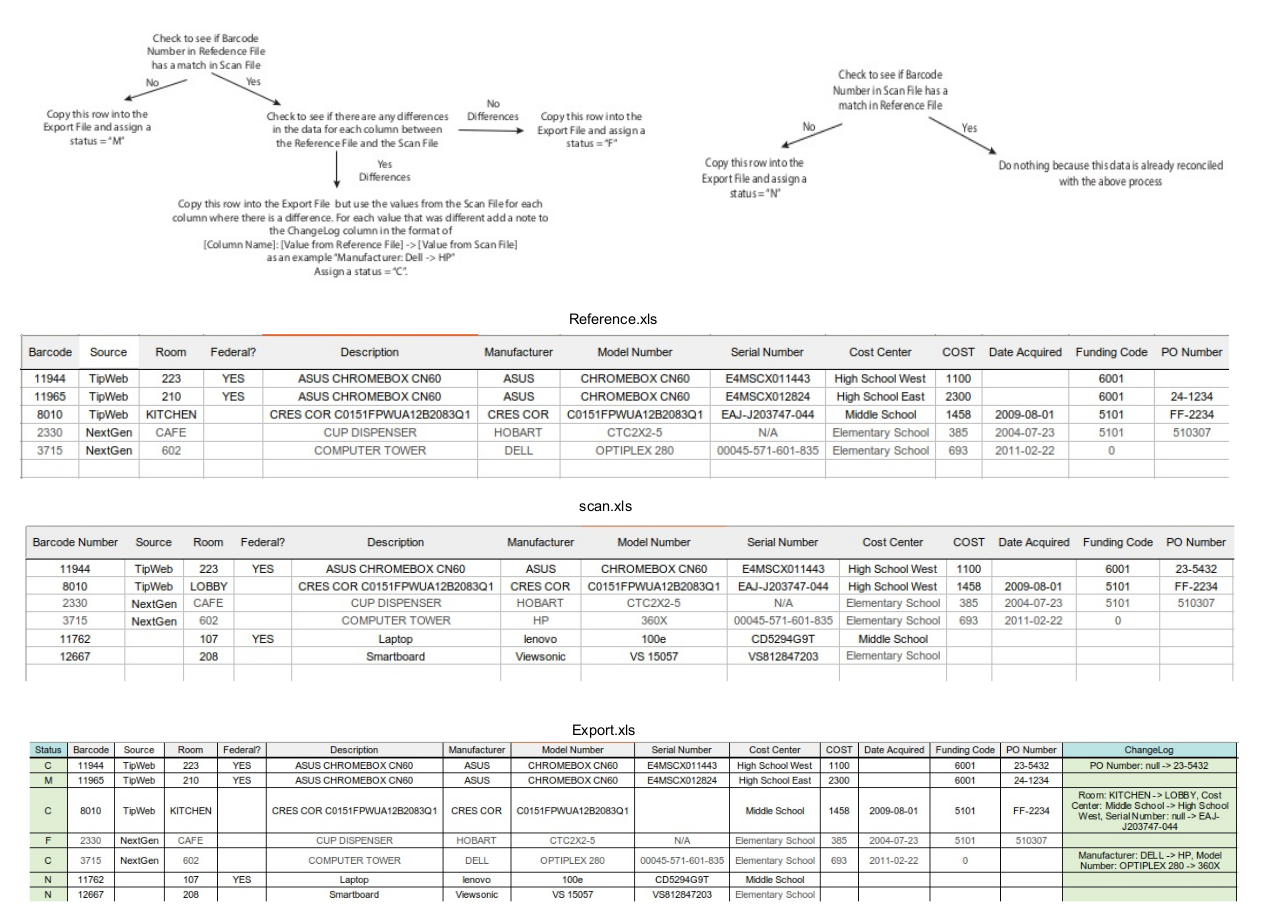
| 8. Merge two excel files based on a column value (e.g. Barcode Number). Report changes in Status and ChangeLog column in the merged file. |
 |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import pandas as pd
import re
import math
import numpy as np
#Given a barcode, this will return the corresponding line & its
#index from the file passed
def get_barcode_line_in_file(bar_code,filename):
fp = open(filename,"r")
lines = fp.readlines()
fp.close()
for line in lines:
# check if string present on a current line
if line.find(str(bar_code)) != -1:
#print('Line Number:', lines.index(line))
#print('Line:', line)
return line,lines.index(line)
#This create a dictionary. Keys are the column name and values are
#the corresponding values in that line related to the index passed
def create_data_dict(data,index):
thisdict = dict()
for x in list(data.columns):
y = data[x][index-1]
flag=pd.isna(y)
if flag == True:
thisdict[x]="NULL"
#print("FFFFFF:",x,y,flag)
else:
thisdict[x]=y
#print(thisdict)
return thisdict
#Create a set of all barcodes in the reference file
referencefile = 'ReferenceFile.csv'
reference_data = pd.read_csv(referencefile)
reference_set = set((reference_data['Barcode Number']))
#print(reference_set)
#Create a set of all barcodes in the scanned file
scanfile = 'ScanFile.csv'
scan_data = pd.read_csv(scanfile)
scan_set = set((scan_data['Barcode Number']))
#print(scan_set)
f = open("export.csv", "w")
j = len(list(reference_data.columns))
#print("J is = ",j)
exportColumnsList = list(reference_data.columns).copy()
#print(exportColumnsList)
exportColumnsList.insert(0,"Status") #Adding Status column in start
#print(exportColumnsList)
exportColumnsList.insert(j+1,"ChangeLog") #Adding ChangeLog at End
#print(exportColumnsList)
f = open("export.csv", "w")
i = 0
j = len(exportColumnsList)
locstr=""
for x in exportColumnsList:
#print("column name=",x,"i is",i)
locstr = locstr+x
if i < j-1:
locstr = locstr+","
else:
locstr = locstr+"\n"
i = i + 1
f.write(locstr)
#Barcode Elements which exists in reference_set but not in scan_set
#are the missing inventory identified by status "M"
#print("Processing M (missing) Inventory present in reference set but not in scan set")
print("================= M (Missing) ==================")
missing_set=reference_set.difference(scan_set)
print(missing_set)
#print("Missing : ",missing_set)
for barcode in missing_set:
locstr="M,"
missing_line,m_index = get_barcode_line_in_file(barcode,referencefile)
#print(missing_line,":",m_index)
m_dict = create_data_dict(reference_data,m_index)
#print(m_dict)
#print("-------------------------")
i = 0
j = len(m_dict)
print("LEN=",j)
for key in m_dict.keys():
m_val = m_dict.get(key)
locstr=locstr+str(m_val)
if i < j-1:
locstr = locstr+","
else:
#locstr = locstr+"\n"
locstr = locstr+",\n" #add , as there is nothing under ChangeLog for Missing inventory
i = i + 1
print(locstr)
f.write(locstr)
#print ("Missing completed")
#Barcode Elements which exists in scan_set but not in reference_set (N - New)
print("================= N (New) ==================")
#print("Processing N (New) Inventory")
new_set=scan_set.difference(reference_set)
print(new_set)
for barcode in new_set:
locstr="N,"
new_line,n_index = get_barcode_line_in_file(barcode,scanfile)
#print(new_line,":",n_index)
n_dict = create_data_dict(scan_data,n_index)
i = 0
j = len(n_dict)
for key in n_dict.keys():
n_val = n_dict.get(key)
locstr=locstr+str(n_val)
if i < j-1:
locstr = locstr+","
else:
#locstr = locstr+"\n"
locstr = locstr+",\n" #add , as there is nothing under ChangeLog for Missing inventory
i = i + 1
print(locstr)
f.write(locstr)
#print("New Inventory completed")
#Barcode Elements which exists in scan_set and in reference_set (could be Found or Changed)
common_set=scan_set.intersection(reference_set)
print(common_set)
#print(list(reference_data.columns))
#print(list(scan_data.columns))
if len(list(reference_data.columns)) != len(list(scan_data.columns)):
print("Error mismatch in columns of reference and scan files")
sys.exit(1)
print("============= F (Found) and C (Changed) cases ================")
for barcode in common_set:
print ("Processing barcode = ",barcode)
reference_line,rindex = get_barcode_line_in_file(barcode,referencefile)
#print(reference_line,":",rindex)
ref_dict = create_data_dict(reference_data,rindex)
print("\n")
print("Ref dictionary")
print(ref_dict)
scan_line,sindex = get_barcode_line_in_file(barcode,scanfile)
print(scan_line,":",sindex)
scan_dict = create_data_dict(scan_data,sindex)
print("\n")
print("Scan dictionary")
print(scan_dict)
print("\n")
if(ref_dict == scan_dict): #perfect match
print("---------FOUND :"+str(barcode)+" ----------------")
locstr="F,"
f_line,f_index = get_barcode_line_in_file(barcode,referencefile)
#print(f_line,":",f_index)
f_dict = create_data_dict(reference_data,f_index)
print(f_dict)
i = 0
j = len(f_dict)
for key in f_dict.keys():
f_val = f_dict.get(key)
print(key,":",f_val,":",type(f_val))
locstr=locstr+str(f_val)
if i < j-1:
locstr = locstr+","
else:
locstr = locstr+"\n"
i = i + 1
print(locstr)
f.write(locstr)
else:
print("---------CHANGE :"+str(barcode)+" ----------------")
locstr="C,"
changestr=""
for rkey in ref_dict.keys():
ref_val = ref_dict.get(rkey)
scan_val = scan_dict.get(rkey)
locstr = locstr+str(scan_val)+","
if ref_val != scan_val:
changestr = changestr+str(rkey)+":"+str(ref_val)+"->"+str(scan_val)+","
locstr = locstr + changestr
locstr = locstr.rstrip(locstr[-1]) #to remove last comma
locstr = locstr+"\n"
print("locstr=",locstr)
f.write(locstr)
f.close()
#print(data)
#print(list(data.columns))
#print(data['Barcode Number'])
#thisset=set((data['Barcode Number']))
#print(thisset)
#print(data.keys)
#print(data.loc[[0,1]])
#print(data.to_string())
|
| 9. Remove lines containing given word from the last paragraph of a file |
#!/usr/bin/python3
# Takes in a path to a folder
# Process all the txt files in folder
# Takes in a pattern word
# Remove the line containing the pattern word from the last paragraph of the txt file
import glob
import os
import shutil
def processfileforpattern(pattern, pathname="./"):
print("Searching for the trigger word : " + pattern)
os.chdir(pathname)
os.mkdir(pathname+"bak")
curdir = os.getcwd()
#print(curdir)
my_files = glob.glob('*.txt')
#print(my_files)
for file in my_files:
print("Processing the file : " + file)
dst = "./bak/"+file
print("Taking backup of the file : " + file + " to " + dst)
shutil.copyfile(file, dst) #taking the backup of the file
linecount = 0
fp = open(file, 'r')
mylist = []
Lines = fp.readlines()
num = len(Lines)
for line in Lines:
linecount += 1
if (linecount == num): #processing the last paragraph
#print (line)
mysubstr = '' #This will store the content of last paragraph without line having trigger word
count = 0
pgphlines = line.split(".") #split this paragraph using at fullstop
pglinesnum = len(pgphlines)
for pgphline in pgphlines:
count += 1
if pattern in pgphline: #skip the line with the given pattern in the last paragraph
continue
else:
if count < pglinesnum:
mysubstr = mysubstr + pgphline + "."
else:
mysubstr = mysubstr + pgphline
#print(mysubstr)
mylist.append(mysubstr)
else:
mylist.append(line)
fp.close()
fp = open(file,'w')
for items in mylist:
fp.write('%s' %items)
fp.close()
processfileforpattern("ecosystem")
|
| 10. Print value of key press on keyboard |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('a.png') # load a dummy image
while(1):
cv2.imshow('img',img)
k = cv2.waitKey(33)
if k==27: # Esc key to stop
break
elif k==-1: # normally -1 returned,so don't print it
continue
else:
print(k) # else print its value
|
Output
-------
Key value (Key name)
32 (Spacebar)
233 (Alt)
97 (a)
225 (Shift)
8 (Backspace)
255 (Delete)
|
| 11. Read csv file into dataframe and print its elements |
#!/usr/bin/python3
import pandas as pd
filename = 'people.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename)
for i in df.index:
print(i,'\t',end='')
txt=''
for j in df.columns:
txt = txt+df.loc[i][j]+"\t"
print(txt.strip())
|
csv file
--------
User Id,First Name,Last Name,Sex,Date of birth
userid-1,Shelby,Terrell,Male,1945-10-26
userid-2,Phillip,Summers,Female,1910-03-24
userid-3,Krist,Travis,Male,1992-07-02
userid-4,Yesen,Martin,Male,2017-08-03
userid-5,Lori,Todd,Male,1938-12-01
userid-6,Erin,Day,Male,2015-10-28
userid-7,Kather,Buck,Female,1989-01-22
userid-8,Ricardo,Hinton,Male,1924-03-26
userid-9,Dave,Farrell,Male,2018-10-06
userid-10,Isaiah,Downs,Male,1964-09-20
Dataframe
---------
0 userid-1 Shelby Terrell Male 1945-10-26
1 userid-2 Phillip Summers Female 1910-03-24
2 userid-3 Krist Travis Male 1992-07-02
3 userid-4 Yesen Martin Male 2017-08-03
4 userid-5 Lori Todd Male 1938-12-01
5 userid-6 Erin Day Male 2015-10-28
6 userid-7 Kather Buck Female 1989-01-22
7 userid-8 Ricardo Hinton Male 1924-03-26
8 userid-9 Dave Farrell Male 2018-10-06
9 userid-10 Isaiah Downs Male 1964-09-20
pd.read_csv : read csv into dataframe
df.index : return the labels of the row. If there are no lables, it return RangeIndex object
df.columns : return the labels of the columns. If there are no lables, it return RangeIndex object
df.loc : The loc property gets, or sets, the value(s) of the specified labels in row and columns
|
|
|